Air quality observations onboard commercial and targeted Zeppelin flights in Germany – a platform for high-resolution trace-gas and aerosol measurements within the planetary boundary layer
Ralf Tillmann, Georgios I. Gkatzelis, Franz Rohrer, Benjamin Winter, Christian Wesolek, Tobias Schuldt, Anne C. Lange, Philipp Franke, Elmar Friese, Michael Decker, Robert Wegener, Morten Hundt, Oleg Aseev, and Astrid Kiendler-Scharr
Abstract
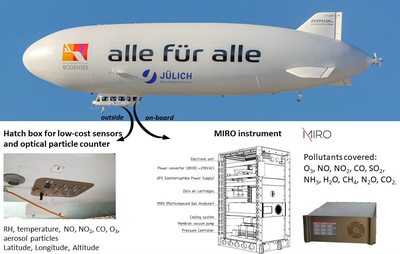
A Zeppelin airship was used as a platform for in situ measurements of greenhouse gases and short-lived air pollutants within the planetary boundary layer (PBL) in Germany. A novel quantum cascade laser-based multi-compound gas analyzer (MIRO Analytical AG) was deployed to simultaneously measure in situ concentrations of greenhouse gases (CO2, N2O, H2O, and CH4) and air pollutants (CO, NO, NO2, O3, SO2, and NH3) with high precision at a measurement rate of 1 Hz. These measurements were complemented by electrochemical sensors for NO, NO2, Ox (NO2 + O3), and CO, an optical particle counter, temperature, humidity, altitude, and position monitoring. Instruments were operated remotely without the need for on-site interactions. Three 2-week campaigns were conducted in 2020 comprising commercial passenger as well as targeted flights over multiple German cities including Cologne, Mönchengladbach, Düsseldorf, Aachen, Frankfurt, but also over industrial areas and highways.
