Correction Strategies for Tissue Voxel Composition in single-voxel MRS: Application in the Quantification of the Neurochemical Profile of the Human Putamen
Ana Gogishvili, Ezequiel Farrher, Christopher E. J. Doppler, Aline Seger, Michael Sommerauer, and N. Jon Shah
2nd June 2023
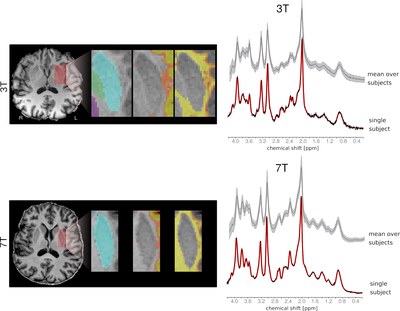
The primary objective of the study was to quantify the metabolic profile of the human putamen in vivo within a cohort of elderly subjects. The putamen was chosen due to its central role in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. Employing single-voxel proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), the team achieved quantification of metabolite concentrations specific to the putamen using a correction method previously proposed to account for tissue composition within the volume of interest. Furthermore, a comparison with the conventional approach that assumes equal concentration across both grey matter (GM) and white matter (WM) was performed. As a means of validation, the metabolic profiles were quantified at two magnetic field strengths, namely 3 Tesla (T) and 7 T.
The study involved the acquisition of spectra from 15 subjects, with an average age of 67.7 ± 8.3 years, at 3 T and 7 T MRI. The spectra were acquired using an ultra-short echo time, stimulated echo acquisition mode sequence (STEAM). To robustly estimate the metabolite concentration ratio between white matter (WM) and grey matter (GM), an additional five subjects were included, deliberately shifting the MRS voxel from the putamen to encompass a broader area of surrounding WM.
The concentrations and WM-to-GM concentration ratios for 16 metabolites were reliably assessed. Notably, the ratios ranged from approximately 0.3 for γ-aminobutyric acid to around 4 for N-acetylaspartylglutamate. Furthermore, the investigated correction method demonstrated significant changes in concentrations compared to the conventional method when the ratio significantly deviated from unity. The research also demonstrated that differences in tissue voxel composition alone could not entirely account for the observed concentration variations between the 3 T and 7 T MRI scanners.
These findings pave the way for further research and open up new avenues to precisely and accurately explore the metabolism of the putamen and, consequently, its role in the context of aging and neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson's disease. The knowledge gained from this study lays a solid foundation for future investigations aimed at elucidating the complexities of the putamen and its role in disease progression, ultimately leading to improved diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.